ガイド付きの術者・患者個別の手術
目視不能の目標を管理する
ガイド付きの術者・患者個別の手術
目視不能の目標を管理する
ExactechGPS ® Guided Personalized Surgery
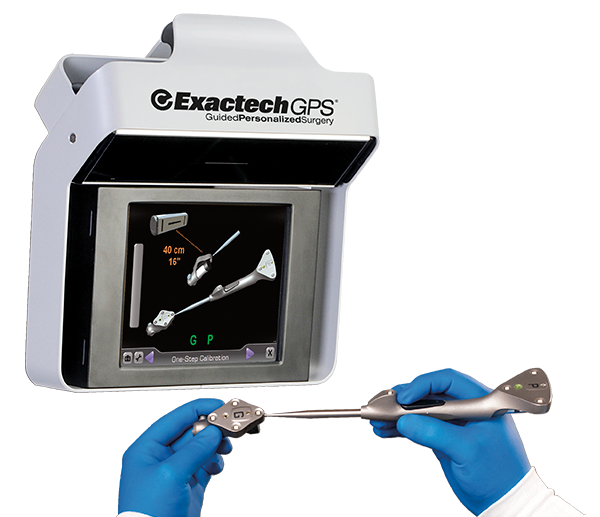
ExactechGPS® はコンパクトで、かつ術者の手元で全ての術中操作が可能な、再現性の高い人工関節置換術を可能にするコンピューター支援手術技術です。
独自のソフトウェアと革新的な専用手術器械との融合により、ExactechGPSは患者さまのQOLが改善するように、個別の患者さまに適合する正確な手術情報を術中にリアルタイムに提供します.
主な特長
ExactechGPS® はコンパクトで、かつ術者の手元で全ての術中操作が可能な、再現性の高い人工関節置換術を可能にするコンピューター支援手術技術です。
個別化
- 骨切りの計画、誘導、確認のための情報がリアルタイムに得られ、術者が好む手術手技にカスタマイズ可能な操作手順
- 最適な解剖学的ランドマークの術中登録を可能にするイメージレス テクノロジー
- 術者の様々なニースに対応する合理的な手術器械のオプション
効率性
- 清潔域に設置されるタブレット型のタッチパネル式ディスプレイと専用カメラを一体化した、アクセスが容易で見通し線の改善
- Disruption, 中断、リアルタイム情報のロスを避けために設計されたアクティブトラッカー方式と手術器械
- ExactechGPSを使用した手術時間は、従来の手術器械を使用した場合と比べて同等であることが示されています11
再現性
- 1㎜または1度 未満2の高度な精度と正確性2
- インプラントの正確なサイズ計測や回旋位を含む位置決めをサポート
- アライメントのリアルタイムフィードバックと骨切り評価

人工膝関節置換術のための コンピュータ支援手術(CAS)の利点:
CASは、以下のことが示されています:
- 短期転帰を改善3
- 再置換の低減4
- 出血量の低減5
- より低いDVT合併率6
- 術後疼痛の軽減7
- 入院期間の短縮8
- Pasquale P. (2014) Navigated Total Knee Arthroplasty Is No Slower than Conventional Instrumented TKA. Presented at the 2014 ICJR Transatlantic Orthopaedic Congress.
- Data on file at Exactech.
- Rebal et al. Imageless Computer Navigation in Total Knee Arthroplasty Provides Superior Short-Term Functional Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis. J. Arthroplasty. 2013 Oct 17.
- Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. Annual Report 2014.
- Conteduca et al. Blood Loss in Computer-Assisted Mobile Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty. A Comparison of Computer-Assisted Surgery with a Conventional Technique. Int Orthop. 2009 Dec 3.
- Siu et al. Lower Post-operative D-Dimer Level in Navigation-assisted TKA than in Conventional TKA: A Prospective Randomised Control Study. J Bone Join Surg, 2015.
- Gothesen et al. Functional Outcome and Alignment in Computer-Assisted and Conventionally Operated Total Knee Replacement: A Multicentre Parallel-Group Randomised Controlled Trial. Bone Joint J. 2014 May 9.
- Dutton et al. Computer-Assisted Minimally Invasive Total Knee Arthroplasty Compared with Standard Total Knee Arthroplasty. A Prospective Randomized Study. J Bone Join Surg, 2008.